Conventional Refinance Loan Requirements 2021
 A
conventional loan is a mortgage that meets the lending guidelines
of the Federal Home Loan Mortgage Corporation (Freddie Mac) and
the Federal National Mortgage Association (Fannie Mae).
A
conventional loan is a mortgage that meets the lending guidelines
of the Federal Home Loan Mortgage Corporation (Freddie Mac) and
the Federal National Mortgage Association (Fannie Mae).
Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae, in theory, compete with each other for
the purchase of mortgages from banks and other lenders. These two
companies are protected from default by the Federal government.
Unlike the government backed home loans, FHA, VA, and USDA mortgages
conventional loans do not require a funding fee that is paid at
settlement or financed with the loan amount. Most
loan officers encourage prospective
borrowers to refinance to a conventional mortgage because the funding
fee cost,
mortgage
insurance premium (if applicable) and other considerations.
Most loan officers encourage prospective borrowers to refinance to a conventional mortgage because the funding fee cost, mortgage insurance premium (if applicable) & other considerations. The conventional loan is used to reduce the interest rate & or term or provide cash out
Loan programs
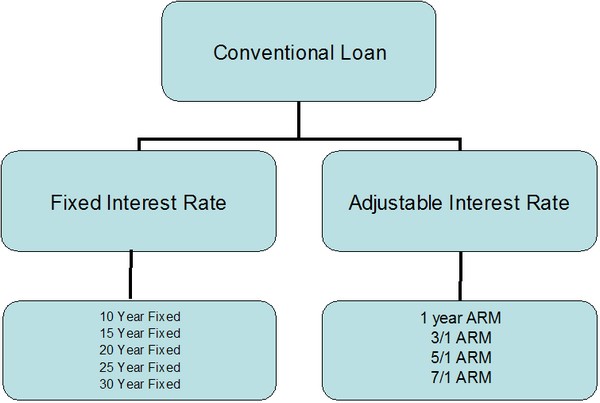
Under the umbrella of the conventional loan program are the loan "types". fixed-rate, adjustable-rate, and a combination of the fixed and adjustable-rate mortgages. Hybrid mortgages (i.e. 3/1, 5/1 & 7/1 arms) are loans that carry a fixed interest rate for a pre-determined number of years, one, three, five or seven-year terms, and then convert to an adjustable interest rate that is subject to change every 12 months. Read more about adjustable-rate mortgages
Limited cash out or cash out
There are two refinance options with the conventional mortgage,
limited refinance and cash out refinance. The limited cash out refinance
is defined as a new loan that is used to pay off an existing first
mortgage loan (including an existing home equity line of credit
in first-lien position); or for single-closing construction-to-permanent
loans to pay for construction costs to build the home, which may
include paying off an existing lot lien. Only
subordinate (2nd and 3rd) liens used to purchase the property may
be paid off and included in the limited cash out mortgage.
If there is a 2nd mortgage (i.e. home equity loan or line of credit)
and it was not used toward the purchase of the property, and the
applicant desires to payoff the second mortgage, the new loan is
classified as a "cash out" refinance. The only other option is to
obtain permission from the 2nd mortgage company to remain in 2nd
position with the new mortgage. Cash out mortgages are usually more
costly and require more equity.
Read more about limited cash-out refinance requirements.
The borrower is permitted to get cash back from a limited cash-out
refinance, but the amount borrowers receive at settlement cannot
be more than the lesser of two percent of the new refinance loan
amount or $2,000. The cash back at settlement can be built
into the new loan amount.
A cash out refinance mortgage is similar to the limited refinance
option, however, this choice permits the payoff of any unpaid principal
balance of the existing first mortgage; the payoff of any outstanding
subordinate mortgage liens of any age; taking equity out of the
subject property that may be used for any purpose.
Read more about cash out refinance mortgages.
How much can I borrow?
The following chart details the equity requirement for limited and cash out loans. For example, the limited cash out loan payoff plus closing costs (if financed) should not exceed (ideally) 95% of the appraised value. Ex. $100,000 X 95% = $95,000 (payoff + closing costs). The cash out option requires 20%% equity. That means that the loan payoff (if applicable) and closing costs should not exceed $80,000.
| Owner Occupied Residence | Number of Units | fixed-rate and adjustable-rate |
|---|---|---|
| Limited Cash-Out Refinance | 1 unit | 97% fixed-rate (conditions apply) 95% adjustable-rate |
| 2 unit | 15% (or more) - equity required for fixed-rate and adjustable-rate | |
| 3 - 4 units | 25% (or more) - equity required for fixed-rate and adjustable-rate | |
| Cash out refinance | 1 unit | 20% (or more) equity required for fixed-rate and adjustable-rate |
| Cash out refinance | 2 - 4 unit | 25% (or more) equity required for fixed-rate and adjustable-rate |
Loan term
The conventional loan terms are available for 10, 15, 20, 25, and 30-year. The FHA and VA loan programs only allows for 15 and 30-year terms. The USDA only permits a 30-year term. The interest rate is usually lower with the shorter loan term.
Second home or investment property
The conventional loan permits refinancing of second homes and investment properties (1 - 4 residential units). The FHA, VA and USDA loan programs do not permit a second home or investment property refinances.
A second home refinance is only permitted with single-family homes or approved condominiums.
| Second Home | Number of Units | fixed-rate and adjustable-rate |
|---|---|---|
| Limited Cash-Out Refinance | 1 unit | Minimum 10% equity (90% loan to value) |
| Cash out refinance | 1 unit | Minimum 25% equity (75% loan to value) |
| Investment Property | Number of Units | fixed-rate and adjustable-rate |
|---|---|---|
| Limited Cash-Out Refinance | 1 - 4 unit | Minimum 25% equity (75% loan to value) |
| Cash out refinance | 1 unit | Minimum 25% equity (75% loan to value) |
| Cash out refinance | 2 - 4 unit | Minimum 30% equity (70% loan to value) |
Here's how a conventional mortgage refinance is structured:
The loan officer starts the refinance calculation with the loan payoff and usually adds in any additional liens (i.e. lines of credit, home equity loans, etc.). The second step is to add in the closing costs, such as title insurance, settlement fees, lender's fees, etc. The lender will also add in enough property taxes for 6 to 12 months. A new homeowner's insurance policy will be required.
The lender will then divide the total refinance cost by the estimated appraised value.
For example, let's say the loan payoff is 100,000 and the closing costs and real estate taxes add up to $4,000, the total refinance cost is $104,000. And if the estimated home value is $150,000, then dividing $104,000 by $150,000, we get 69% loan to value. That's good. If the loan amount is greater than 80%, the loan would require mortgage insurance.
Monthly mortgage insurance premium
The conventional mortgage requires "mortgage
insurance" when the loan amount is greater than 80% of the appraised
value. For example, if the value of the home is $100,000 and the
loan amount is $90,000, mortgagee insurance is required. If the
loan amount is $80,000 or less, no mortgage insurance is required.
Mortgage insurance on a conventional loan should not be confused
with life insurance. The proceeds of a life insurance policy is
paid to the beneficiary on the death of the insured. Mortgage insurance
is paid to the bank or lender if there is a default on the loan.
There are several payment plans with private mortgage insurance.
The most popular payment plan is the monthly payment. The mortgage
insurance premium decreases with the equity in the home.
Conventional loans (usually) have higher loan amounts
Another advantage of the conventional mortgage is the increased
loan amounts. Each year the Federal Housing Finance Agency (FHFA)
establishes the maximum lending limit for conventional loans and
the government mortgages. For most US counties, the maximum loan
limit for conventional loans is 35% higher than the FHA mortgage.
The lending limit increases with two, three, and four-unit residential
properties. The VA single-family loan limit is the same as the conventional
loan limit for a one-unit dwelling. The VA does not have higher
lending limits for 2 - 4 unit owner occupied properties. The USDA
does not impose a lending limit, however, the USDA has other guidelines
that lower the loan amount for a refinance mortgage.
When the loan amount exceeds the lending limit of Fannie Mae and
Freddie Mac, the loan is known as a
jumbo loan. Jumbo
mortgages cannot be sold to either Fannie Mae or Freddie Mac due
to the purchase limitation. The lender holds the loan in the mortgage
portfolio or sells the loan to a lender who is willing to accept
the risk. Since there is a risk with holding on to a high-value mortgage,
the interest rate is increased.
Loans are said to "conform" when the loan amount is at or below
the Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac lending limits and meet the agency's
lending guidelines. Lenders will use term conventional conforming
loan to describe a conventional loan that meets the guidelines and
meets the lending limits set by the Federal Housing Finance Agency.
Conventional loan interest rates
You might be surprised to know that the interest rate on conventional
loans are "adjusted" based on the applicant's credit score, whether
the refinance mortgage is a limited refinance or a cash out loan.
Cash out loans cost more. Two to four-unit properties cost more,
low credit scores increase the interest rate or closing costs. Fannie
Mae calls interest rate adjustments "Loan
-Level Price Adjustments". Freddie Mac also adjusts the interest
rates based on similar factors. Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac do not
originate conventional mortgages, but purchase loans that meet their
lending guidelines. The interest rate adjustments are sent down
to the lender, who usually pass the additional cost to the borrower.
See today's interest
rates